Public good or public bad? Nation-building and Indigenous institutions

Abstract: While existing evidence shows that nation-building policies unify societies, little is known about how and what makes some societal groups to resist them. We examine this in the context of the post-Mexican Revolution (1920s–1950s), when the new state implemented a nation-building policy to eliminate Indigenous cultures and identities by increasing connectivity via transport infrastructure. […]
The Aftermath of Sovereign Debt Crises: A Narrative Approach
Abstract: This paper investigates the causal effects of sovereign debt crises in a sample of 50 defaulting economies between 1870 and 2010. As default is potentially endogenous, we use the narrative approach to identify plausibly exogenous episodes. We find economically and statistically significant costs of up to 3.2 percent of GDP before recovering to the […]
Speculation in the UK, 1785-2019
Abstract: Speculation has long been thought to have significant economic effects, but it is difficult to measure, making it challenging to examine these effects empirically. In this paper we measure speculation in the UK since 1785 by using business and financial reporting in The Times newspaper. Our monthly speculation index reveals four distinct epochs of […]
On the persistence of persistence: Lessons from long-term trends in African Institutions

Abstract: An influential strand of literature within economics and economic history called ‘persistence studies’ argues that low material living standards in African countries today were determined by institutional choices made in the past. However, the lack of consistent annual data on GDP per capita or institutional variables has meant that this literature has been largely […]
Why are corporations terminated? A century of evidence from the Netherlands

Abstract: We identify all 196 Dutch exchange-listed corporations that halted their operations and ceased to exist between 1903 and 1996. We then explain these terminations using unique hand-collected accounting and governance data and regression techniques suited to long-run comparative analysis. Although Dutch bankruptcy laws remained unchanged across the twentieth century, patterns of corporate exit shifted […]
The CEO: The Rise and Fall of Britain’s Captains of Industry

The CEOs of Britain’s largest companies wield immense power, but we know very little about them. How did they get to the top? Why do they have so much power? Are they really worth that exorbitant salary? Michael Aldous and John Turner provide the answers by telling the story of the British CEO over the […]
Quarterly GDP for Ireland Since 1950
Abstract: We construct estimates of quarterly GDP for Ireland from 1950, linking to official data from 1995 onward, using a novel factor-augmented Chow-Lin interpolation. Compared to the only alternative series (OECD, 2025), our procedure exploits the variation in a large number of official quarterly economic data and our estimates are broadly consistent with contemporary reports. […]
Applying History to Inform Anticipatory AI Governance: Using Foresight and Hindsight to Inform Policymaking

Summary: Artificial intelligence (AI) heralds societal changes that could rival those associated with past transformational general-purpose technologies, such as metallurgy, the steam engine, electricity, and the internet. As with such technologies, AI offers the opportunity for tremendous increases in human well-being while also threatening to destabilize social, governance, economic, and critical infrastructure systems and disempower […]
Rural electrification and secondary school enrolments in Ireland

Abstract: Electrification influences economic choices, not least by allowing households to replace labour with capital and to enhance domestic labour productivity. We test whether newly electrified households invested more in children’s human capital formation, proxied by secondary school enrolments, under Ireland’s Rural Electrification Scheme (1947-1966). IV panel regressions examine whether electrification led to higher per […]
Religion and Economic Development: Past, Present, and Future

Abstract: This chapter examines the role of religion in economic development, both historically and today. Religion’s influence varies globally, with high religiosity in countries like Pakistan and low rates in China. Despite declines in some Western countries, religion remains influential worldwide, with projected growth in Muslim populations due to higher fertility rates. Religion continues to […]
Taking a Punt: Monetary Experimentation and the Irish Macroeconomic Crisis of 1955-56
Abstract: The 1955-56 macroeconomic crisis is a central event in modern Irish history. Yet, despite this centrality, its causes are not clearly understood. In 1955-6, Ireland, which had previously followed British interest rates in lockstep as part of its fixed exchange with the latter, briefly experimented with independent monetary policy. Our contribution is twofold. First, […]
Zombie International Currency: The Pound Sterling 1945–1971

Abstract: This paper examines the international role of sterling during the Bretton Woods era and argues that it was not a competitor to the U.S. dollar. I construct a novel dataset to measure the reserve role of sterling in Europe and sterling area countries. The postwar reserve role of sterling was limited to the sterling […]
Forced Migration and Local Economic Development: Evidence from Postwar Hungary

Abstract: We investigate the effects of forced migration on sending economies using the post-WW2 expulsion of German minorities from Hungary as a natural experiment. We combine historical and contemporary data sources to show that the forced migrations led to lasting reductions in economic activity. Plausible mechanisms driving this result appear to be sectoral change (shift […]
Housing Prices, Costs, And Policy: The Housing Supply Equation In Ireland Since 1970

Abstract: This article examines the responsiveness of new housing supply to prices and costs, using the case of Ireland at quarterly frequency from the 1970s, as well as a county-level panel from the 1990s. Across four error-correction specifications, and supported by an instrumental variables approach, we find the estimated elasticity of new housing supply to […]
The rise and fall of urban concentration in Britain: Zipf, Gibrat and Gini across two centuries

Abstract: City size and growth are the subject of a substantial literature in economic geography and urban economics, but consensus remains elusive on the extent to which key regularities such as Zipf’s Law or Gibrat’s Law holds across space and time. We contribute to this literature by examining city size, rank and growth in Britain […]
Rueff Versus de Lattre: A French Money Doctors’ Duel for Influence Over de Gaulle

Abstract: In the early sixties, the U.S. and U.K. balance of payments deficits threatened the stability of Bretton Woods international monetary system. Jacques Rueff campaigned for its termination and the return to a system based only on gold, as in the nineteenth century. He encouraged French president Charles de Gaulle to publicly advocate the abandonment […]
Irish GDP Since Independence

Abstract: This paper constructs annual GDP estimates for Ireland (1924-47) to join the first complete official aggregates. The new series is deployed to revisit Ireland’s economic performance in the post-independence decades. Ireland’s economy grew at 1.5 per cent per annum and average living standards improved by 40 per cent. The bulk of this was due […]
Three Centuries of Corporate Governance in the UK

Abstract: As articulated by Adam Smith, one of the central issues facing companies is that managers will not run the business in the interests of its owners and will misuse resources. This ultimately has a detrimental consequence for the wealth of the nation. This survey reviews the nature and evolution of the corporate governance of […]
The Regional Location of Indigenous and Foreign Manufacturing Establishments, 1929-1975
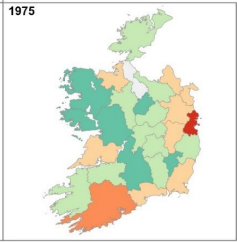
Abstract: Regional industrial location has been a matter of intense political interest throughout the history of the state. Details of the geographic distribution of manufacturing establishments are sparse however – particularly up to EEC accession – as reporting of the relevant data was heavily constrained by the requirement to maintain firm level confidentiality. Our research […]
What can we learn from historical pandemics? A systematic review of the literature

Abstract: What are the insights from historical pandemics for policymaking today? We carry out a systematic review of the literature on the impact of pandemics that occurred since the Industrial Revolution and prior to Covid-19. Our literature searches were conducted between June 2020 and September 2023, with the final review encompassing 169 research papers selected […]
Banks and the Economy: Evidence from the Irish Bank Strike of 1966
Abstract: This paper studies a natural experiment in macroeconomic history: the Irish bank strike of 1966, which led to the closure of the major commercial banks for three months. We use synthetic control to estimate how the economy would have evolved had the strike not happened. We find that economic activity slowed, deviating by 6% […]
Social housing and the spread of population: Evidence from twentieth century Ireland

Abstract: How does housing policy influence the long-run distribution of population? We examine the impact on long-term population dynamics of the world’s first large-scale rural public housing scheme, specifically the case of Ireland’s Labourers Acts. We link detailed data on the location of over 45,000 heavily subsidized cottages for agricultural laborers built 1883–1915 in over 200 […]
Aristocratic Amateurs to Fat Cats? British CEOs in the Twentieth Century

Abstract: This article uses a prosopographical methodology and a new dataset of 1,558 CEOs from Britain’s largest public companies between 1900 and 2009 to analyse how the role, social background, and career pathways of corporate leaders changed. We have four main findings: First, the designation of CEO only prevailed in the 1990s. Second, the proportion […]
Should History Change The Way We Think About Populism?

Abstract: This paper asks whether history should change the way in which economists and economic historians think about populism. We use Müller’s definition, according to which populism is ‘an exclusionary form of identity politics, which is why it poses a threat to democracy’. We make three historical arguments. First, late 19th century US Populists were […]
Tracing Sustainability In The Long Run: Genuine Savings Estimates 1850 – 2018

Abstract: We introduce a new database of historical Genuine Savings (GS), an indicator of sustainable development promoted by the World Bank and widely used in contemporary economic research. GS derives from the theoretical work on wealth accounting, and addresses shortcomings in conventional metrics of economic development by incorporating broader measures of saving and investment, including […]
The Nationalist Dilemma: A Global History of Economic Nationalism, 1776–Present

Summary: Nationalists think about the economy, Marvin Suesse argues, and this thinking matters once nationalists hold political power. Many nationalists seek to limit global exchange, but others prioritise economic development. The potential conflict between these two goals shapes nationalist policy making. Drawing on historical case studies from thirty countries – from the American Revolution to […]
Economic Penalties based on Neighborhood, and Wealth Building
Abstract: Building wealth over lifetimes became possible for a broader span of the population in developed countries over the 20th century compared to any time in history. This was driven by more people having the capacity to save because of the expansion of middle-class jobs and education, access to highly developed financial markets, and government […]




